Taxation of Fringe Benefits received by Employees

In this article, we shall cover taxation of Fringe Benefit. A fringe benefit is a form of pay for the performance of services of value besides wages that employers provide to employees. Sometimes, employers give fringe benefits to attract& retain employees. Any fringe benefit received by employees is taxable and must be included in the recipient’s gross income unless the law specifically excludes it.
There are 2 types of Qualifying Fringe Benefits, ones that allow discrimination & ones that don’t allow discrimination and both are treated differently in the hands of the recipient.
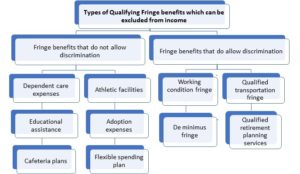
(A) Fringe benefits that do not allow discrimination – In this context, “Discrimination” implies it means that in order for these fringe benefits to be excluded from Gross Income of the recipient, it must be offered to all employees equally in the organization and should not favour one set of employees over another.
Various types of fringe benefits that do not allow discrimination are
- Dependent care expenses – Under this type of Fringe Benefit, an employer can directly pay upto a certain Dollar amount of dependant care expenses related to qualifying child or qualifying relative on behalf of the employee.
- Educational assistance –Here, the value of educational assistance forundergraduate and graduate education of employees is excludible up to a certain dollar amount. In such cases, the payment made must only be for tuition, fees, books, and supplies, and not for room and board.
- Cafeteria or flexible benefits plans – This allows employees to pick and choose between certain non-taxable benefits or cash. If cash is chosen, the amount received is taxable, but if a non-cash benefit is chosen, the benefit remains non-taxable.
- Athletic facilities – Value of use of athletic facilities can be excluded from gross income of employees, if the facility is located on the located on the premises of the employer and open equally to all employees alongwith their employees.
- Adoption Expenses – Here, employee adoption expenses paid by the employer or reimbursed by the employer to the employee are excludible from the employee’s gross income. This effectively allowsthe employer to help pay for these expenses on behalf of the employee. However, this phases out as the employee’s adjusted gross income, or AGI, reaches a certain threshold (which changes from year to year)
- Flexible Spending Plan– Under this type of fringe benefit, employees can opt to receive lower cash compensation from their employers in return for their employer agreeing to pay certain costs on behalf of the employee without the employee recognizing income. FSAs provide employees a way to use tax-free dollars to pay medical expenses not covered by other health plans. Throughout the year, employees can then use funds to pay qualified medical expenses not covered by their health plan, and to pay for a variety of medical products and services ranging from dental and vision care to eyeglasses and hearing aids. However, employees must use the amount in the FSA or lose the unused part of pre-tax dollars.
(B) Fringe benefits that not allow discrimination – What do we mean when we say discrimination?
The word “Discrimination” in this context implies that these fringe benefits are always excludable from the employee’s gross income, even if the benefits are not offered to all employees in the organization. This means these fringe benefits can be provided only to senior executives.
Some fringe benefits that do allow discrimination are –
- Working condition fringe – This is an expense that would be deductible as an employee business expense if paid for by the employee. Here, when an employer pays for the cost of an expense incurred by the employee, but had the employee paid for the cost him or herself, it would have been deductible. For instance, the value of the business use of a company provided car by an employee is excludable as a working condition fringe benefit. To substantiate the claim of business use, the employee must maintain an accurate mileage log which includes a written record of the total miles driven and a breakup of personal & business travelled distance.
- De minimis fringe – It is a type of fringe benefit, whose accounting is unreasonable and impractical. Because its value and the frequency with which it is provided, is so small. In determining whether a benefit is de minimis, one should always consider its frequency and value. A De minimis fringe benefit can be provided to certain employees and not others. Examples include Occasional tickets for entertainment events or allowing an senior executive to make a few copies using the copying machine
- Qualified Transport Fringe – This is again a type of fringe benefit that can be provided on a discriminatory basis to select employees. Here an employer can pay directly or reimburse select employees for transit expenses, transit passes or qualified parking expenses. A transit pass includes a bus pass, a subway pass, a rail pass and a qualified parking includes covering the parking fees for certain employees.
- Qualified retirement planning services – This fringe benefit covers the value of any retirement planning advice or information provided by an employer who maintains a qualified retirement plan. Hence, the value that a retiring employee gets in terms of investment or retirement advice is excludable from the employee’s gross income.


